Periapical and Periodontal Abscess
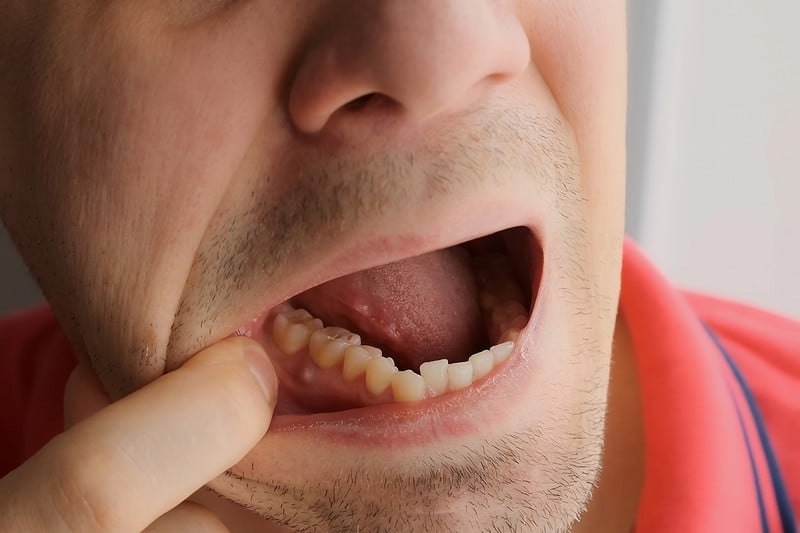
Infection of the dental pulp leads to a periapical abscess. The pulp is the living tissue in a tooth that includes the nerves, blood vessels, and connective tissue. Inflammatory diseases in the dental pulp or the peri radicular tissues surrounding a tooth are the most common causes of sudden, severe tooth pain.
Abscesses at the gum line around a tooth’s apex are often caused by an untreated cavity, an injury, or a wrong dental procedure. An abscess at the root tip may result from infection, irritation, and swelling. In the event of severe, permanent infection, the necrosis of the pulp might extend across the whole pulp cavity. When the pulp dies, an infection may spread into the pulp chamber. Apical periodontitis is an inflammatory reaction in the periapical tissues brought on by the human defense system in response to a pulp infection.
Pathogens trapped in periodontal pockets or next to emerging teeth beneath the operculum, a soft tissue flap, may also lead to periodontal abscess and wisdom tooth disease. Furthermore, an opening might form between the tooth abscess and the maxillary sinus. It can also lead to sepsis, a systemic infection. If the pus level rises, the tissue pressure increases, and an abscess may perforate neighboring tissues.










