A toothache is characterized by discomfort in the area of the teeth and jaws and can either be intermittent or persistent. The pulp is the soft tissue and blood vessel-rich substance found inside a tooth that has the most delicate nerves in the body. Painful dental problems like cavities and gum disease may also be caused by bacteria that thrive in the mouth. When the nerve in the tooth’s root or in the gums becomes inflamed, the result is a painful toothache. It can also be due to an infection, decay, accident, or the loss of a tooth. Moreover, toothache may be a symptom of pain that originates elsewhere but radiates to the jaw, such as the temporomandibular jomt (TMJ), ear, and sinuses.
Sometimes it’s hard to tell whether a toothache is in the upper or lower jaw. Pain in a lower molar tooth sometimes seems to originate in the ear. Some mistakenly attribute pain in their upper teeth to their sinuses, the air-filled cavities that sit behind the cheeks and forehead.
Similarly, the intensity of the discomfort varies, and the onset is often described as sharp and unexpected. When tooth discomfort persists for more than two days, it’s best to see a dentist as soon as possible to prevent further damage to the surrounding tissues.
Tooth Abscess
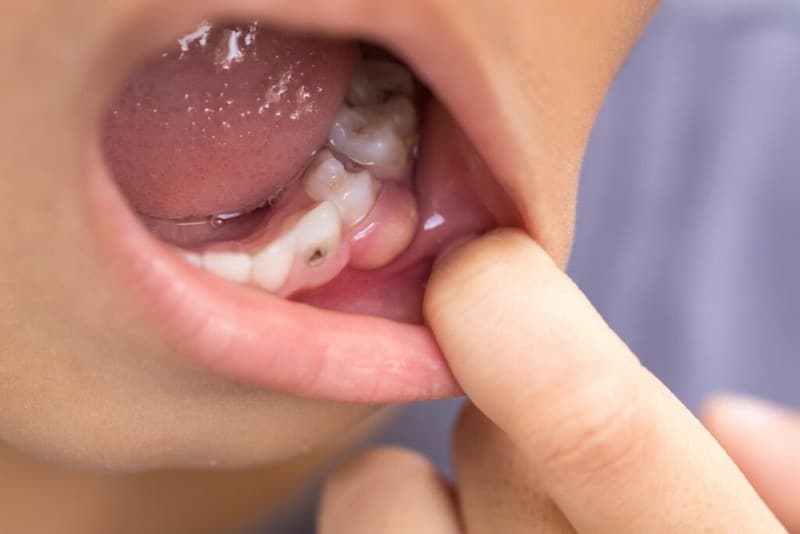
An abscess is a pus-filled pocket in the gums or jawbone around an infected tooth which can form in several locations. When bacteria enter the root tip, it causes an abscess wherein an infected bone may suffer bone loss. The pulp chamber, the hollow center of a tooth, may get infected if a cavity progresses far enough into the tooth due to dental work, such as a crown or if the tooth sustains physical stress.
This condition may cause severe, throbbing pain that can develop quickly and worsen over time. Consequently, the root infection caused by the abscess is usually accompanied by puffy gums and disabling pain. Discomfort radiates from an infected tooth or gum to the adjacent jaw and neck, affecting daily activities and disrupting sleep. Sometimes, medication cannot help with the pain associated with it.
It may also cause discoloration or reddening of the gums, sensitivity to pressure around the afflicted tooth, and sharp, constant pain. Pus may gather in the teeth, gums, or jawbone supporting the teeth, resulting in a dental abscess. Abscesses don’t heal on their own, so it’s crucial to get medical attention as soon as possible. Endodontic treatment or dental extraction may be necessary, depending on the severity of the situation.










