Fatty liver disease or hepatic steatosis is a medical condition wherein extra fat surrounds the liver. There are two types of hepatic steatosis – non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and alcohol-related fatty liver disease (AFLD). Experts also categorize NAFLD into simple fatty liver and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). Meanwhile, AFLD can cause an enlarged liver, alcoholic hepatitis, or alcoholic cirrhosis.
Research states that heavy drinking, defined as having three or more glasses of alcoholic beverages per day, can be among the primary causes of alcohol-related fatty liver disease. However, even if a person doesn’t drink, they can still develop non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, especially if they have diabetes or carry too much weight. Doctors also point out that having a metabolic syndrome, such as insulin resistance, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, or hypertriglyceridemia, can increase the risk of developing fatty liver disease.
Although early-stage NAFLD isn’t considered dangerous, it can lead to severe conditions such as liver cirrhosis, kidney problems, hypertension, and diabetes complications. Typically, fatty liver disease doesn’t manifest many symptoms, but doctors can use ultrasound or CT scans to get a picture of the liver.
Here are some of the symptoms of fatty liver disease.
Ascites
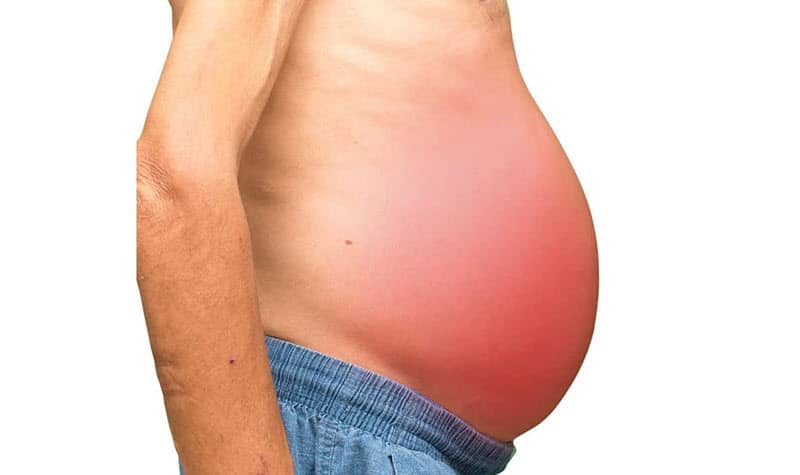
People who may have hepatic steatosis can manifest with ascites. Ascites are a condition where fluids collect in spaces within the abdomen. It can be pretty painful if the disease has elevated in severity. In addition, ascites can cause abdominal inflammation and infection and may even move into the chest and lungs, making breathing difficult.
Doctors say that ascites indicate liver cirrhosis, although they can also mean that the person may have low protein levels or different types of cancer. Ascites can also suggest that the person may need dialysis or may have a heart condition.
A person who suffers from ascites may experience bloating, weight gain, abdominal swelling, a sense of heaviness, swelling of the lower legs, and hemorrhoids. With treatment and medication, it is possible to reverse the effects of ascites temporarily. However, more invasive surgery will be needed to reverse the effects as time passes, and ultimately, they may need a liver transplant.










