Osteoporosis
Vitamin D is an essential nutrient that the body needs for many different functions. It plays a vital role in bone health. A deficiency in vitamin D can lead to osteoporosis, a condition that causes bones to become weak and fragile.
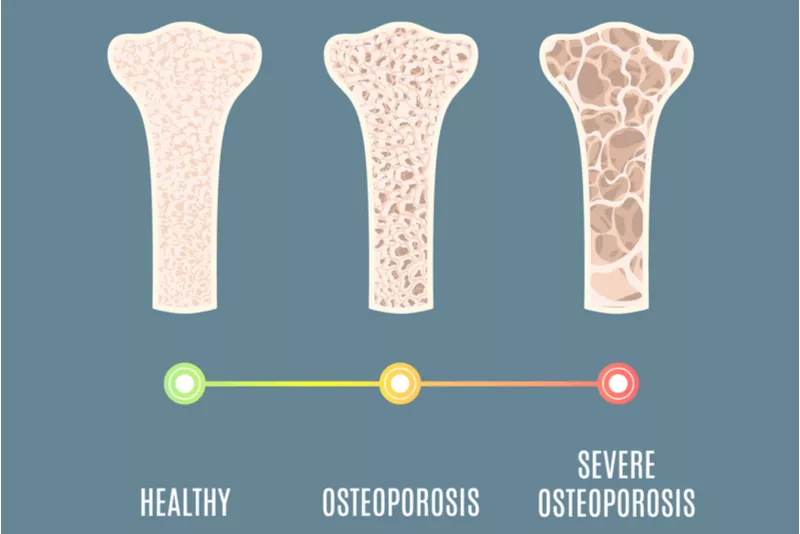
Osteoporosis happens when the body does not make enough new bone or when too much old bone is lost. The most common type of osteoporosis happens as people get older. Women are more likely to develop osteoporosis than men because they have less bone mass to start with, and they lose bone mass more quickly as they age.
Other risk factors for developing osteoporosis include being Caucasian or Asian, having a family history of the condition, smoking cigarettes, drinking too much alcohol, and having certain medical conditions such as celiac disease or rheumatoid arthritis.
One of the main ways that vitamin D affects the body is by helping it absorb calcium from food. Calcium is important for strong bones. Vitamin D deficiency can lead to osteoporosis by causing the body to absorb less calcium from food. It can also cause the body to make less new bone and lead to bone loss.










