Receding Gums
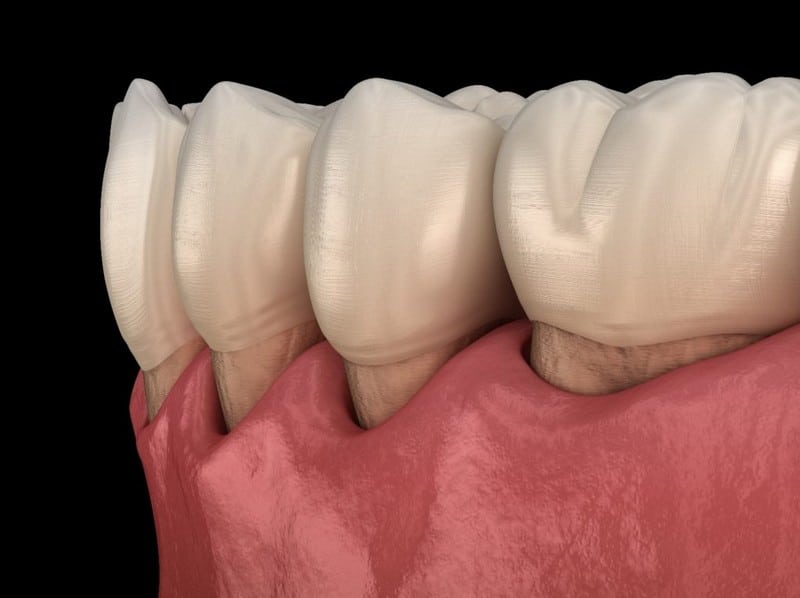
Gum recession is the condition through which gum tissue recedes from the teeth, exposing the tooth roots. Tooth sensitivity is the primary indicator of gum recession. Roots of teeth that are exposed due to gum recession are vulnerable to temperature extremes, such as those found in hot and cold drinks. Increased sensitivity to sugary foods will occur when more of the tooth and nerves become exposed. Another obvious indication is that your teeth seem longer than usual.
Moreover, gum recession creates a space between the tooth and gum that may harbor harmful germs and food particles. As a result, bacteria, plaque, and food particles may readily accumulate in these crevices and eventually cause infections, gum disease, tooth decay, and even tooth loss.
Exposed tooth roots are another potential source of infection and discomfort. Gum recession makes teeth less secure in the mouth, which may lead to tooth loss if left untreated. The receding of the gums is subtle and usually goes undiscovered until severe dental issues arise. Unfortunately, it’s impossible to restore gum tissue after the recession has begun. Gum recession is a serious dental health problem that requires medical attention to avoid complications in oral health.










