Cellulitis
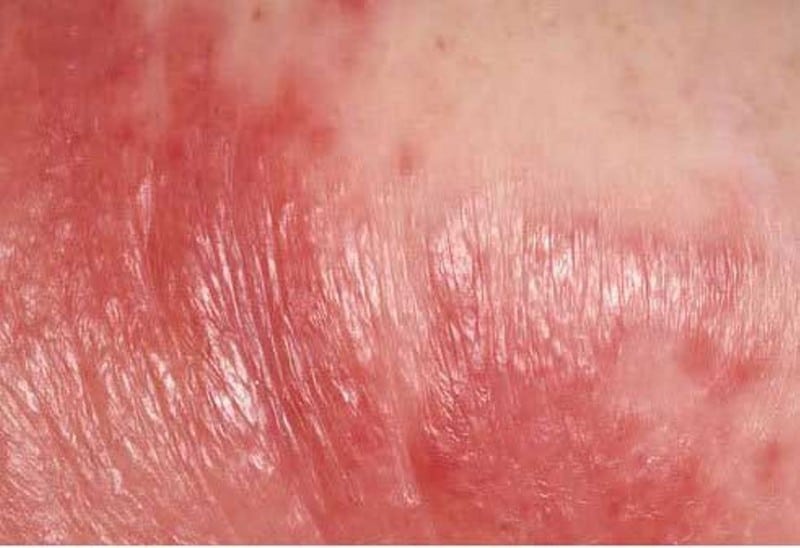
Cellulitis is one of the most common bacterial infections that occur on and under the skin of the tissues. When there is an open entry on the skin, like a crack, scrape or cut obtained through insect and animal bites, eczema, small wounds, surgical wounds, or athlete’s foot, the bacteria can enter, and the affected area starts to become hot, swollen, and painful to touch. It can be noticed by a gradual change in the skin color: skin with a lighter complexion appears to be reddish or pinkish, while in darker tones, grayish or purplish.
Most of the time, it affects the face, hands, arms, legs, feet, and other body parts. The infection can be mild or severe, but when left untreated, it can spread to the bloodstream and the lymph nodes, which naturally react to infection, and could lead to further health complications or death. In addition, cellulitis does not transmit from one person to another, though it rarely happens. Therefore, it is best to make sure wounds and cuts are well-cleaned and disinfected to prevent bacteria from getting into the outer layer of the skin. If signs of cellulitis are noticed, seek medical help immediately.










