Angioedema
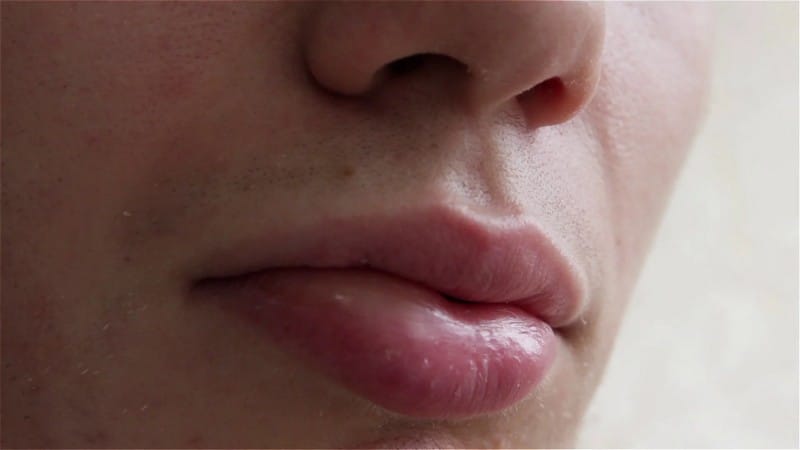
Angioedema is often similarly categorized with hives (also known as urticaria), which makes the swelling occur underneath the skin and not on the surface. It usually affects both the outer and inner skin layers on the face and the throat. It may be caused by a reaction to harmful substances, allergies from food or medicines, a side effect from another disease, exposure to much sunlight, pet dander, insect bites, pollens, dust, and dirt particles carried by the wind, or hereditary.
People with angioedema usually experience swelling in the eyes, lips, airways, throat, neck, or face. The gradual growth of red splotches on the skin or cheeks (like welts) is also noticeable and stinging pain in the affected area. It is best to avoid the consumption of substances that might trigger an allergic reaction and always maintain a healthy skin condition by putting on protective creams and gear. When symptoms of angioedema are seen, it is best to consult the doctor and ask for treatments that can help subside the pain and heal the infected areas. Though it can easily develop in a person’s skin, it cannot be transmitted from one person to another.










