Herpes Zoster Ophthalmicus
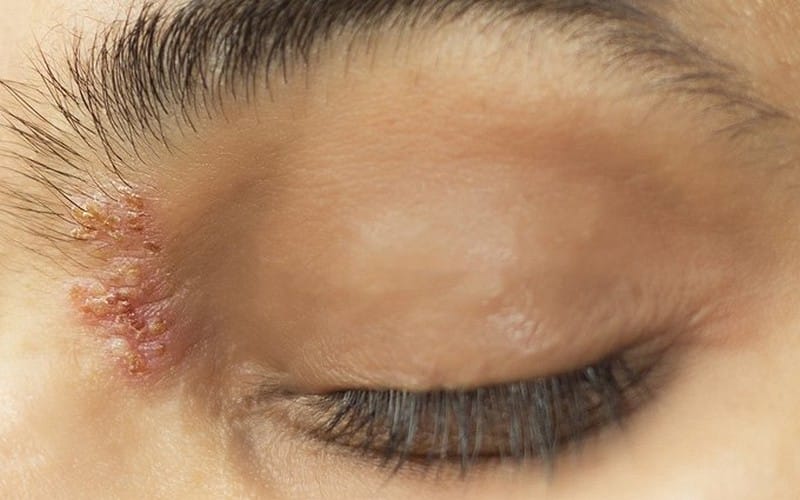
Herpes zoster ophthalmicus (HZO), more commonly known as shingles, is a disease characterized by painful, blistering rashes in the forehead, nose, and upper eyelid, resulting from the chickenpox virus that escaped from the nerve cells. While the blisters caused by the disease usually go away in 7 to 10 days after it crusts and falls off, the pain remains for at least one to three months for some people. It also causes other eye problems, including swelling, redness, sensitivity to light, and blurry vision. In the worst cases, shingles can lead to vision loss or blindness.
Unlike chickenpox which usually affects children, shingles are generally observed among people beyond 50 years old or those with weakened immune systems like people with autoimmune diseases and HIV.
As far as treatment goes, shingles usually require 7 to 10 days of home treatment, taking oral antiviral pills, applying steroid drops in cases of significant inflammation, applying eye drops or ointments, and putting cool, wet cloth to relieve the pain and itching in the affected area. In severe cases, it may require hospitalization.










