Lymphadenitis
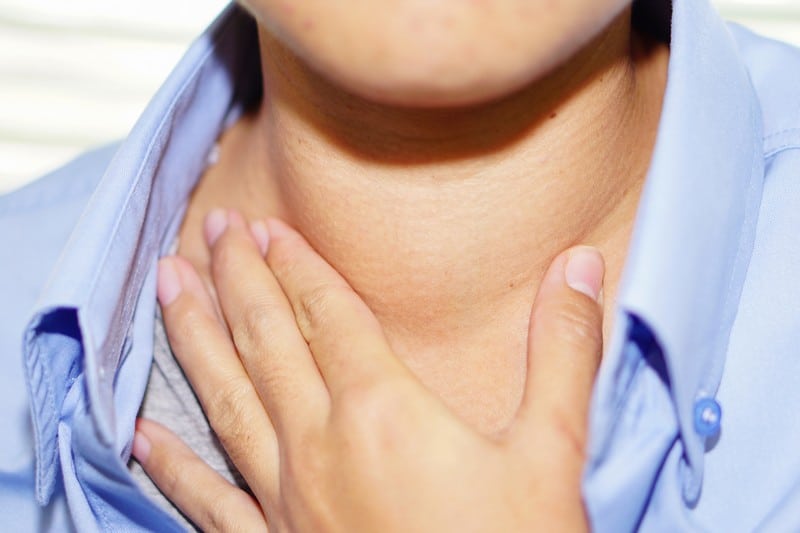
Lymphadenitis, or the inflammation of the lymph nodes, can develop for different reasons, the most common of which are bacterial infections like strep throat and a cold. Specific cancers like lymphoma or leukemia may also result in swollen lymph nodes. Depending on their location and triggers, the condition can cause various symptoms. These include swollen and tender lymph nodes, upper respiratory issues like a sore throat and runny nose, limb swelling, night sweats, and the expansion and hardening of your lymph nodes.
Often, the treatment of the condition depends on the underlying cause. In specific cases, no further treatment is necessary. For example, those whose bodies are healthy and overpower the infection don’t need medical treatment. In case treatment is needed, it will vary based on the condition’s severity and your overall health. In mild cases, fever-reducing painkillers like ibuprofen may be prescribed. Antibiotics may also be recommended.
If the lymph nodes become infected, abscesses may form. For the swelling to go down, draining may be required. The procedure is usually done by cutting the affected area to allow the infected pus to drain. Once it’s over, the healthcare provider may use gauze for healing.










