Atherosclerosis
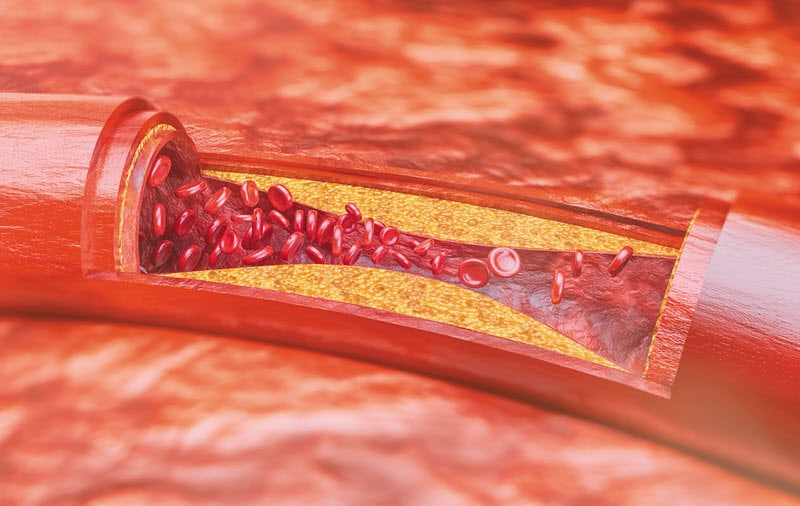
Atherosclerosis refers to the narrowing of the arteries because of the accumulation of plaque, which are substances made up of cholesterol, calcium, and fats. The buildup restricts or obstructs blood flow and may occur in arteries throughout the body. It can result in oxygen and blood shortage, increasing risk of infection and development of conditions like ringworm. It’s also possible for pieces of the plaque to break off, causing blood clots. The disease can result in heart attacks, and strokes.
The symptoms of the condition often don’t appear until an obstruction occurs. These include angina or chest pain, cramps, breathlessness, fatigue, confusion, loss of sensory or motor function, and muscle weakness. In the case of a heart attack or stroke, some symptoms that may precede its onset are chest pain, weakness in the limbs or face, pain in the jaw or arm, and lightheadedness.
When plaque accumulates, and the arteries begin to inflame and harden, it makes it harder for blood to travel throughout the body, preventing tissues and organs from adequate oxygenated blood. Some of its causes are high cholesterol and aging. Treatment is generally a combination of dietary changes and medications. In severe cases, surgery may be necessary.










