Prostate infection, or prostatitis, is a condition where the walnut-shaped gland that forms the component of the reproductive system of males becomes infected and inflamed. It’s not an uncommon problem, and it can cause various symptoms, including but not necessarily limited to difficulty urinating and pain. The two types of this medical issue are acute and chronic. The former is the short-term prostate infection that generally accompanies severe symptoms, while the latter is long-term and may go and come.
Some symptoms of acute prostatitis are unpleasant odors of the urine, blood in semen or urine, body aches, difficulty and pain while urinating, chills or fever, frequent urination, and nausea. On the other hand, pain in the bladder, lower testes, and abdomen may accompany the condition. Often, it’s diagnosed using blood tests, urine and semen analysis, imaging tests, and biopsies. With these tests, healthcare providers can confirm the diagnosis and exclude or rule out different disorders. Moreover, it can help determine the best course of action for treating the condition.
Those who have symptoms of a prostate infection must get immediate treatment or risk complications occurring. Some of these are abscesses, bacteremia, chronic pain, epididymitis, infertility, and urinary problems.
Obstructive Uropathy
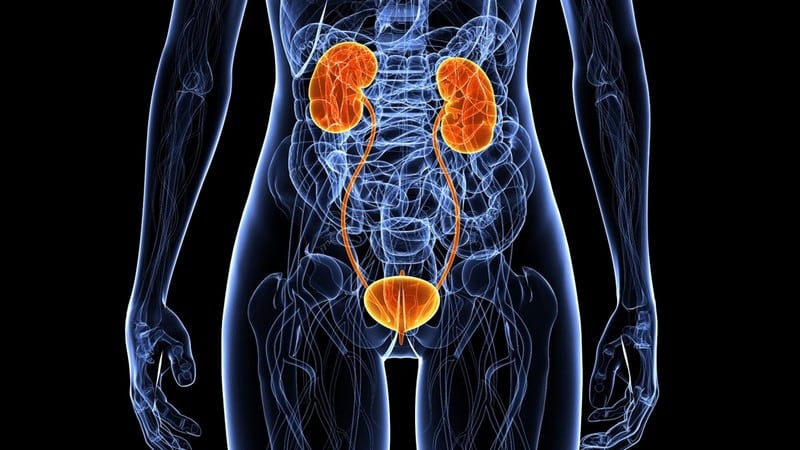
Obstructive uropathy refers to the inability of urine to flow through the urethra, bladder, and ureter due to an obstruction. It can be either an entire or partial blockage. Rather than flowing to the kidneys from the bladder, it goes back or refluxes into the pear-shaped organs. The two tubes responsible for carrying urine from the kidneys to the bladder are called ureters, and the condition can result in swelling or damage to these organs.
Various factors can bring about obstructive uropathy. Permanent or temporary blockages in the urethra or ureter, through which the urine exits the body, may result from injuries like pelvic fractures, digestive tract diseases, kidney stones, and tumor masses on the colon, uterus, bladder, or kidneys. It’s also possible for nervous system-related disorders to cause the condition. Enlarged prostates are another frequent trigger for obstructive uropathy in men.
Symptoms to look out for in obstructive uropathy are difficulties passing urine, slowed or dribbled streams, nocturia or frequent urges to urinate at night, feelings of a full bladder, and blood in the urine. You may also experience a decrease in urine output if one kidney is obstructed. It can also cause complications if untreated.










