Sarcoidosis
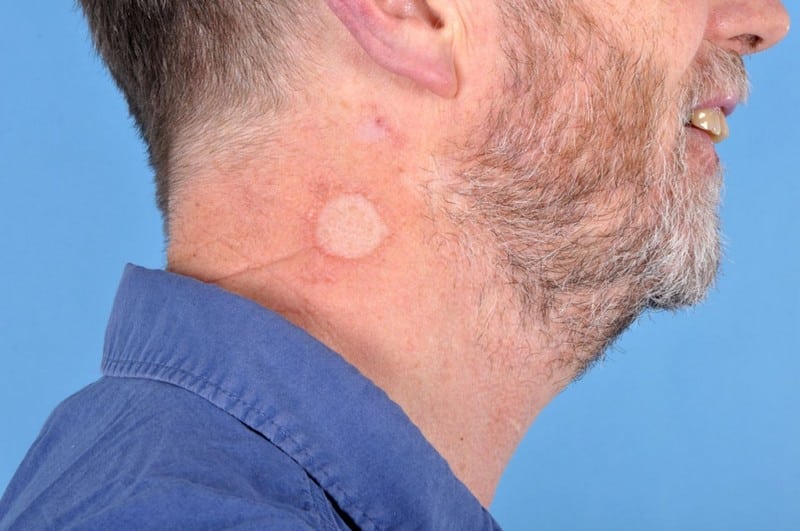
Sarcoidosis occurs whenever granulomas, or inflammatory cell clumps, begin forming in different organs. The condition is usually triggered by the immune system’s response to foreign elements and substances like chemicals, viruses, and bacteria. The areas most commonly affected are the lymph nodes, lungs, eyes, skin, liver, heart, spleen, and brain. While most people don’t experience any symptoms, some of the signs of the disease include fatigue, fever, weight loss, joint pain, nosebleeds, abdominal swelling, rash, and skin lesions.
The symptoms of sarcoidosis generally depend on the affected area or organ. For example, if it occurs in the gastrointestinal system, it may cause gastritis and stomach pains. If it’s the respiratory system, like the lungs, symptoms may include a dry cough, breath shortness, and wheezing. The primary cause of the disease is still unknown, but studies have shown race, genetics, and sex to be risk factors for sarcoidosis.
It’s also not easy to diagnose sarcoidosis because many of its symptoms are similar to other conditions. But most healthcare providers will diagnose the condition by checking for a rash or skin bumps, swollen or irritated lymph nodes, listening to the lungs and heart, and checking for enlarged spleen and liver.










