Use of Catheter
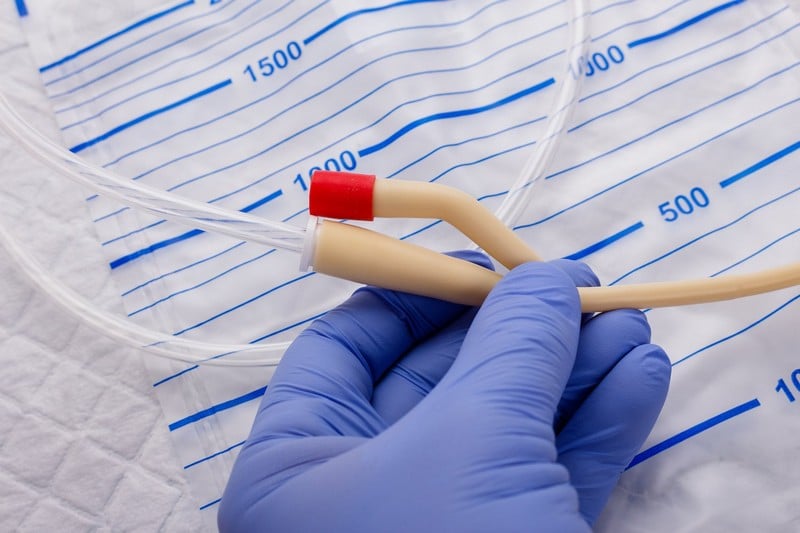
The National Healthcare Safety Network (NHSN) reports that UTIs are the most prevalent healthcare-associated type of illness. A urinary catheter—a tube put into the bladder via the urethra to empty urine—is connected to about 75 percent of UTIs contracted while a patient is hospitalized.
Urinary catheters are given to between 15 and 25 percent of hospitalized patients. Prolonged use of urinary catheters is the leading risk factor for acquiring a catheter-associated UTI (CAUTI). Therefore, catheters must only be used when necessary and should be taken out as quickly as possible.
A catheter could remain in for a long time. In this case, it is referred to as an indwelling catheter. A UTI in the kidneys or bladder is more likely to occur in those who have an indwelling urinary catheter.
A catheter-related UTI may result from a variety of bacteria or fungi. With conventional medicines, treating this form of UTI is more challenging. Urine leakage (incontinence), the inability to empty the bladder, and bladder, prostate, or vaginal surgery are common causes of indwelling catheter use.










