Infected or inflamed hair follicles are a common cause of folliculitis, a skin condition. It might seem similar to acne and be highly uncomfortable. However, the physical signs of folliculitis can have a significant emotional and social impact. Many diverse kinds of folliculitis exist, each with its root cause, infectious agent, and skin effects. It’s possible to develop folliculitis through everyday habits like shaving, soaking in a hot tub, and working outside that cause too much sweat.
Hair is present in almost every part of a human’s anatomy. While others stand out clearly, other strands are so thin that the person might not even realize they’re there. Hair is more functional than just looking good; it keeps us warm. In addition, it functions as an anti-adversarial mechanism in the human body. A follicle is the opening through which hair grows from the skin. In addition to housing oil glands, the strand is an anchor for fine hair.
Unfortunately, follicles are prone to collecting bacteria and other foreign elements that can lead to irritation and infection. It also swells up when inflamed and can cause a visible lump to appear on the skin.
Here are the causes of developing folliculitis.
Shaving and waxing
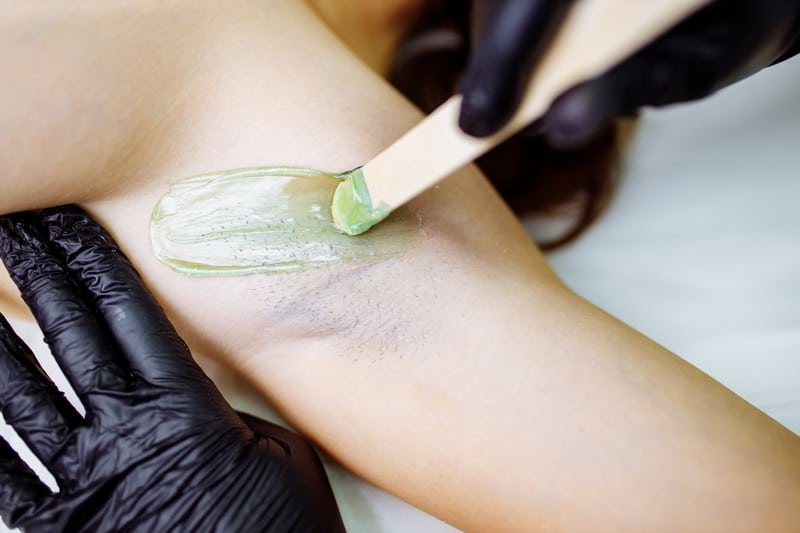
Shaving removes hair by cutting it off with a razor or another bladed instrument, usually but not always down to the skin’s surface. For example, men often shave their beards and facial hair, whereas women typically shave their legs and underarms to eradicate the hairs to be clean-shaven.
Shaving one’s chest, abdomen, legs, underarms, pubic area, or other body hair is a common practice for both men and women.
Shaving and waxing are two practices that might lead to folliculitis. Shaving and waxing both create microscopic incisions in the skin, which opens the door for germs to enter the hair follicles. These then reproduce, causing the afflicted area to develop large, red pimples accompanied by inflammation. In addition, shaving with a dull blade can lead to razor bumps when the hair follicle is nicking. This ailment, known as folliculitis, can occasionally be treated with a specialized safety razor, but it is ineffective for many men. A dermatologist can advise on how to shave off the beard and mustache safely and effectively if patients suffer from folliculitis.










