Pulmonary Embolism
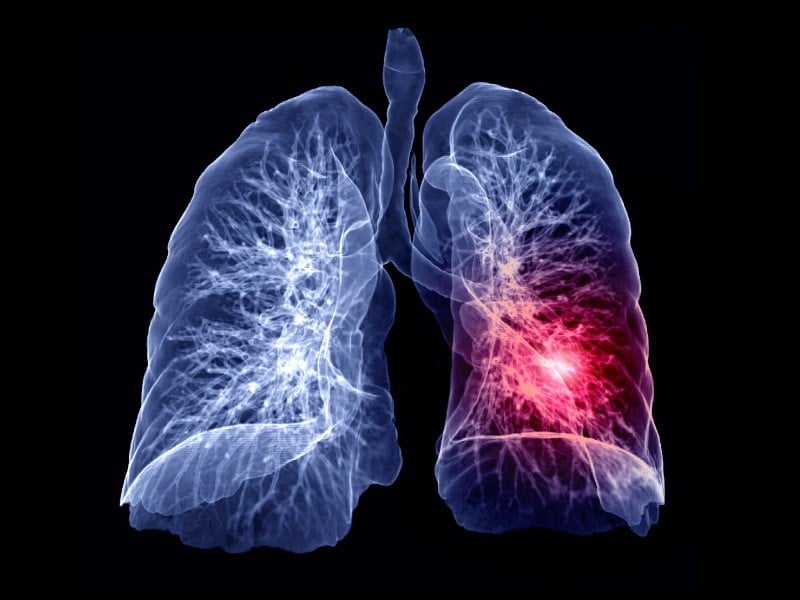
Pulmonary embolisms refer to blockages found in the lung’s pulmonary arteries. In many cases, the blood clots traveling from the leg’s deep veins or other areas of your body toward the lungs cause these embolisms. Since the clots can potentially block the flow of blood, the condition is considered to be life-threatening. However, with suitable treatment options and early diagnosis, it’s possible to reduce the risk of mortality that pulmonary embolism can pose.
The symptoms of pulmonary embolism can vary based on factors like the clot’s size, how much lung is involved, or whether there’s an underlying illness in the heart or lungs. However, the common symptoms and signs typically include breathlessness, chest pains, and coughing. In some cases, the condition may also lead to an irregular or rapid heartbeat, dizziness or light-headedness, sweating profusely, fever, leg pain, and pulmonary edema. Due to the potentially fatal nature of the condition, it’s best to seek immediate medical attention if you experience coughing with bloody sputum, unexplained dyspnea, and chest pain.










