Jaundice
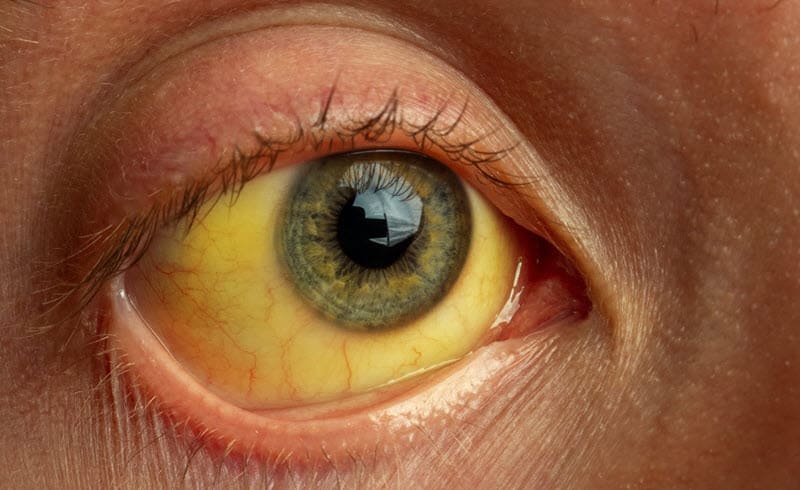
Jaundice is the condition when a person’s eyes, mucus membranes, and skin appear to have a yellowish tinge. The yellow color comes from a substance called bilirubin, a product of the breakdown of old red blood cells. These red blood cells travel to the gallbladder, liver, and gastrointestinal tract before being excreted by the body. Although it is a common condition for newborns, the disorder in adults may signify an underlying problem that needs specialized attention.
Red blood cells die every day. The liver removes the old red blood cells, and the body eliminates them through the stool. Jaundice occurs when the liver becomes overloaded or damaged, leading to the bilirubin not moving correctly into the gastrointestinal tract. Although jaundice can manifest because of infections, gallstones, blood disorders, use of certain drugs, and liver cancer, most of the time, it manifests because of liver diseases such as NAFLD or AFLD.
Jaundice also manifests in the urine and stool. If a person notices that their urine becomes brown or dark-colored, or their stools become pale or clay-colored, there’s a huge chance that they already have jaundice. Although jaundice in itself isn’t dangerous, it needs appropriate treatment. Doctors recommend phototherapy for newborns, blood transfusion, fluid replacement, and intravenous immunoglobulin.










