Ovarian Cysts
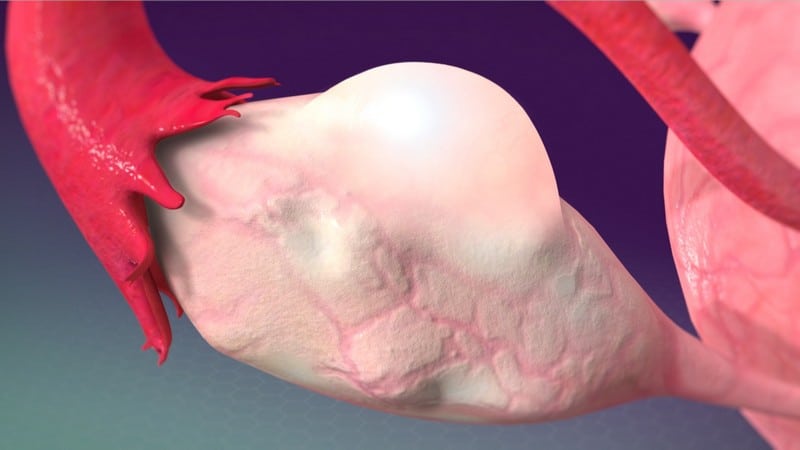
Ovarian cysts are sacs or pockets filled with fluids in the ovary or its surface. They are common and usually form during the childbearing years. Majority of ovarian cysts present no symptoms and disappear on their own. However, some may cause pain or bleeding. An ovarian cyst rupture can cause severe pain or internal bleeding. Surgery may be necessary to remove a large ovarian cyst.
When ovarian cysts become too large, they can cause more severe complications, including an enlarged uterus. The enlarged uterus presses on the bladder, which can cause urinary frequency and urgency. It can also press on the rectum, causing constipation.
An enlarged uterus can also cause back pain and abdominal pain. Treatment for an enlarged uterus caused by ovarian cysts includes over-the-counter pain relievers, heating pads, and rest. In addition, surgery may be necessary to remove the cysts. In some cases, a hysterectomy may be recommended.
While there is no way to prevent the formation of ovarian cysts, it helps to schedule regular pelvic examinations to determine abnormal changes in the ovaries. It is also crucial for women to be more mindful of changes in their menstrual cycle. Changes in menstrual patterns and symptoms or missed periods are tell-tale signs of ovarian cyst formation.










