Ovarian Cancer
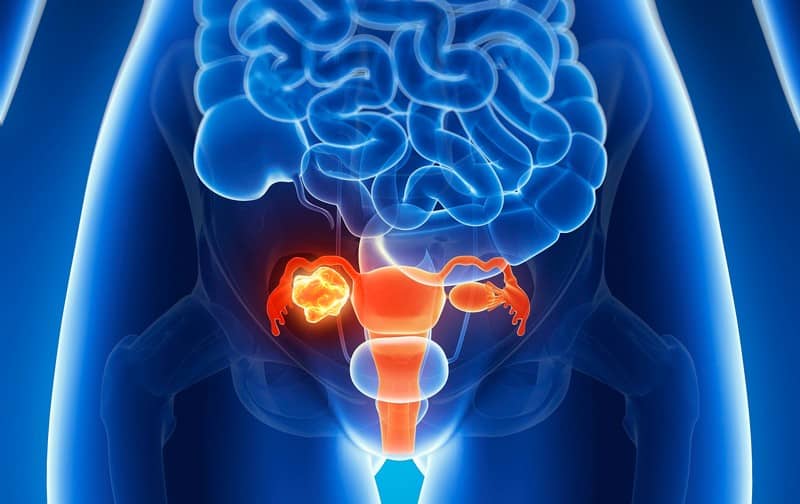
Ovarian cancer is one of the most common cancers in women. Learning about the causes, symptoms, treatment, and prevention strategies for ovarian cancer is crucial to improve a woman’s prognosis. Several ovarian tumors may cause endometrial enlargement and thickening. This condition is due to the estrogenic effects of the malignant ovarian tissues.
The ovaries are a pair of small organs in the pelvis that produce eggs and hormones. Every woman has two ovaries, one on each side of the uterus. Ovarian cancer starts in the ovaries. The most common symptom of ovarian cancer is an enlarged uterus.
Other symptoms may include abdominal pain, bloating, pelvic pain, difficulty urinating, fatigue, back pain, constipation, and irregular menstrual periods. Women who experience one or more symptoms should see a gynecologist for a more comprehensive diagnostic examination.
There are several treatment options for ovarian cancer, including surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy. Prevention strategies for ovarian cancer include maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, eating a healthy diet, and avoiding tobacco products. In addition, women with ovarian cancer with uterus enlargement and other symptoms must talk to their doctors about possible treatment options and ways to prevent cancer from returning.










