Inflamed Tympanic
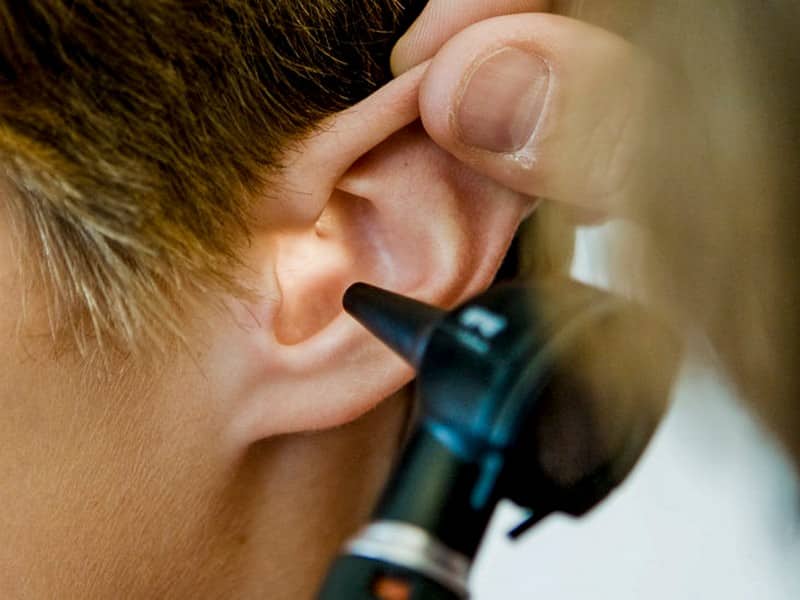
Another possible cause of ear infection is inflammation of the Tympanic membrane, commonly known as eardrum inflammation and referred to in medicine as tympanitis. Several other causes of this membrane inflammation include trauma and microorganisms. The hearing may be significantly impacted if the membrane is irritated.
The tympanic membrane marks the boundary between the middle and external ear, also referred to as the eardrum. The membrane is vibrating, which is what a person hears every day.
The eardrum is a delicate, flexible membrane that spans the ear canal like skin would spread across a drum. This thin membrane that separates the middle ear from the ear canal is crucial to hearing.
The middle ear’s small bones vibrate in response to sound waves striking the eardrum, sending nerve impulses to the inner ear and, ultimately, the brain, where the sounds are decoded. However, sounds don’t typically resonate when the eardrum is inflamed. Pain and distorted hearing result from the swelling.
Speaking and hearing can both be impacted by persistent inflammation or swelling of the eardrum, particularly in young toddlers who depend on clear hearing for accurate speech mimicry.










