Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency
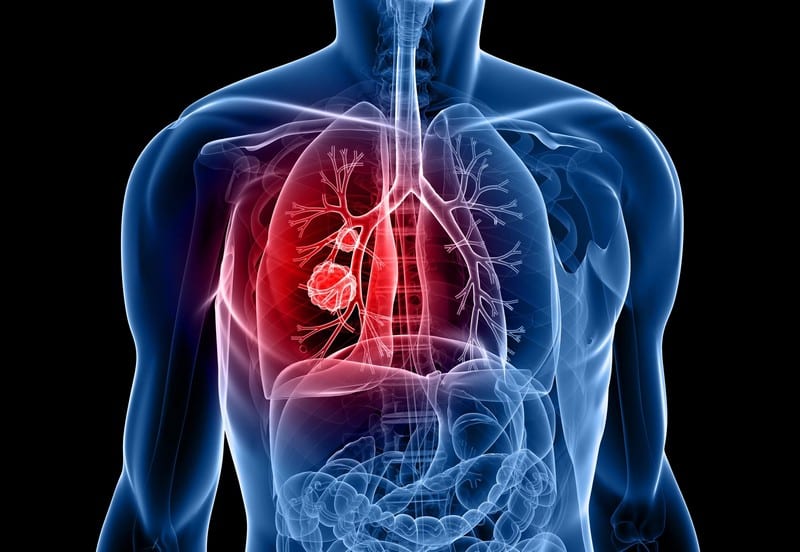
Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency (AATD) is an inherited disorder that primarily affects the lungs and liver. AATD is caused by a mutation in the SERPINA1 gene, which provides instructions for making alpha-1 antitrypsin. This protein is produced mainly in the liver and functions as an enzyme that protects tissues from elastase, a digestive enzyme produced by white blood cells. In people with AATD, the SERPINA1 gene mutation has an abnormal alpha-1 antitrypsin protein that cannot effectively neutralize elastase. As a result, elastase builds up and damages lung and liver tissues.
Most people with AATD have no symptoms until adulthood, when they may develop lung problems such as emphysema or chronic bronchitis. These lung problems are caused by damage to the walls of the alveoli, the tiny air sacs in the lungs where oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged. Liver damage associated with AATD can lead to serious problems such as cirrhosis or liver failure. There is no cure for AATD, but treatment can help manage symptoms and slow down the progression of permanent liver and lung damage.










