Trichomoniasis
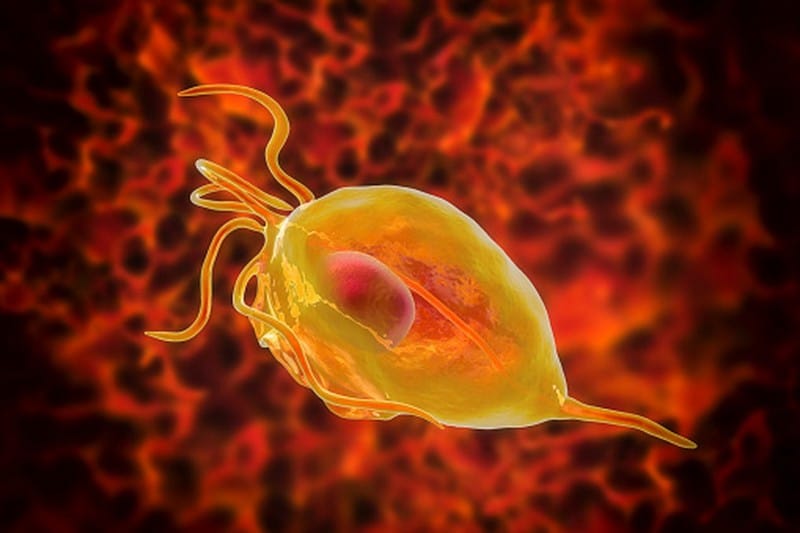
Trichomoniasis is a common sexually transmitted infection caused by a single-celled protozoa called Trichomonas vaginalis. The infection is usually acquired through unprotected sexual intercourse with an infected partner. However, it can also be passed from mother to child during childbirth.
The reason for the unusual vaginal odor is that trichomoniasis changes the composition of vaginal flora. Normally, the vagina contains various bacteria that acidify the vagina and prevent the overgrowth of harmful microbes. However, when trichomoniasis disrupts the normal bacterial balance, it can lead to an overgrowth of bad bacteria. This overgrowth can cause the vagina to smell different than usual.
While trichomoniasis is often asymptomatic in women, some may experience itching, burning, redness and swelling of the genitals, and pain during urination. An unusual vaginal odor is one of the most common symptoms of trichomoniasis. This odor is often described as being fishy or foul-smelling.
The discharge associated with trichomoniasis may also be thicker than normal and may be yellowish, greenish, or brownish. In some cases, the discharge may contain blood. Trichomoniasis is easily treated with antibiotics, but it can become re-infected if sexual intercourse is resumed before both partners have completed treatment.










