Herpes Simplex Virus
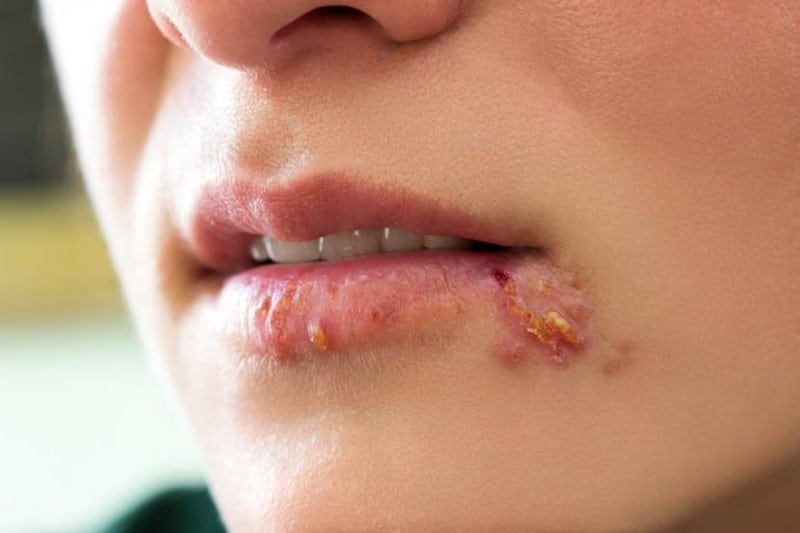
Herpes simplex virus is a microorganism that infects humans. HSV-1 is typically associated with orofacial infections, while HSV-2 is associated with genital infections. Both types of HSV can cause recurrent infections. The viruses are transmitted through direct contact with infected skin or mucous membranes.
Transmission can occur from an asymptomatic infected person or an infected person with active symptoms. Both types of herpes simplex virus can infect the oropharynx and cause tonsillitis. Herpes simplex virus is spread through close contact with someone with an active infection. The virus can be spread through saliva, mucus, or skin contact, kissing, or sharing eating utensils with someone who has an active infection. It can also be spread through contact with infected objects, such as towels, razors, or toothbrushes.
People with active infection are most contagious during times when they are experiencing symptoms. However, it is possible to spread the virus even when no symptoms are present. While most cases of tonsillitis caused by herpes simplex virus resolve on their own within a few days, some people may experience more serious complications, including abscesses, dehydration from difficulty swallowing, or airway obstruction from large tonsils.










