Worms are parasites that live in the digestive tracts of animals. They are transmitted through contact with infected feces. The most common worms to infect humans include roundworms, hookworms, and tapeworms. Certain worms only infect humans.
Worms can potentially cause various illnesses in humans, including intestinal obstruction or peritonitis. Other symptoms of worms in humans include abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, and abdominal swelling. In some cases, worms can cause anemia or malnutrition.
An average human may get several intestinal worms from consuming contaminated food or water or being bitten by a host animal such as a cat or dog. In addition, some infections can be passed to humans through sexual contact or the inhalation of eggs from feces in the air.
Let us explore all the possible symptoms of these parasitic organisms in humans.
Worms in Excrement
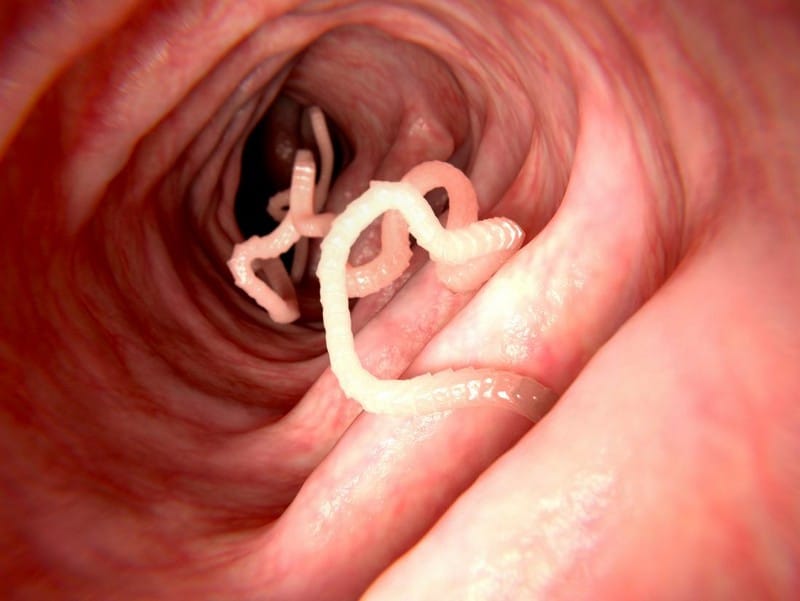
Worms in excrement are a symptom of worms in humans. While doctors can analyze human feces in a lab to determine if they contain any parasites, they may not be present, or the adult parasite may have already passed out of the body. So it is important to look for other symptoms when determining whether a person has worms.
One way to tell whether someone has worms is by evaluating the consistency and color of their stool, the waste product that exits the body after digestion. A change in stool color or consistency is sometimes the first sign that a person has worms.
The most common worm species to cause this type of symptom is Ascaris. Ascaris causes intestinal obstruction and malnutrition because it lives and feeds off nutrients inside your intestines.
To effectively treat worm infestation, it is important to determine which type of worm you are infected with since different types require different treatments. The diagnosis process can be lengthy and may involve stool tests to detect eggs or larvae in your stool samples.










