Dental Bone Grafting
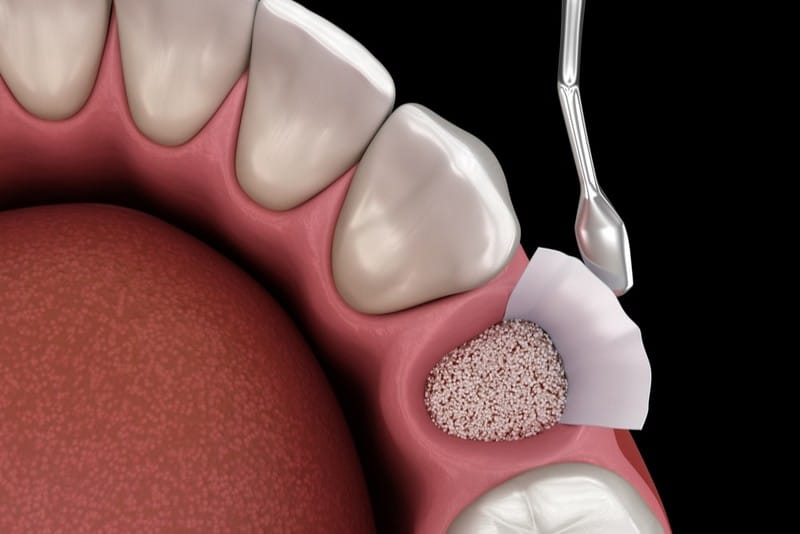
Dental bone grafting is the process of adding more density and volume to the jaw, specifically in the areas where bone losses have occurred. The material of the bone graft may come from your body or be purchased from tissue banks. In some cases, it can also be synthetic. The purpose of bone grafting is to hold the space or gap for the body to begin repairing it, similar to a scaffold in which bone tissue will regenerate and grow. Dental providers combine the process with platelet-rich plasma or PRP to promote tissue regeneration and healing.
Those with losses of bone in their jaws are usually the ones who require the bone grafting procedure. It’s also recommended for tooth extractions, dental implants to replace missing teeth, rebuilding the jaws for dentures, and receding gums. The four types of bone grafting are socket preservation, ridge augmentation, and periodontal. The procedure will be determined by what the patient requires.
Usually, bone grafting procedures begin with the application of a local anesthetic. Next, a small incision is created in the gums so the jawbone can be visible. After disinfecting and cleaning the area, the material for bone grafting is added to address the defect.










