Tissue Swelling
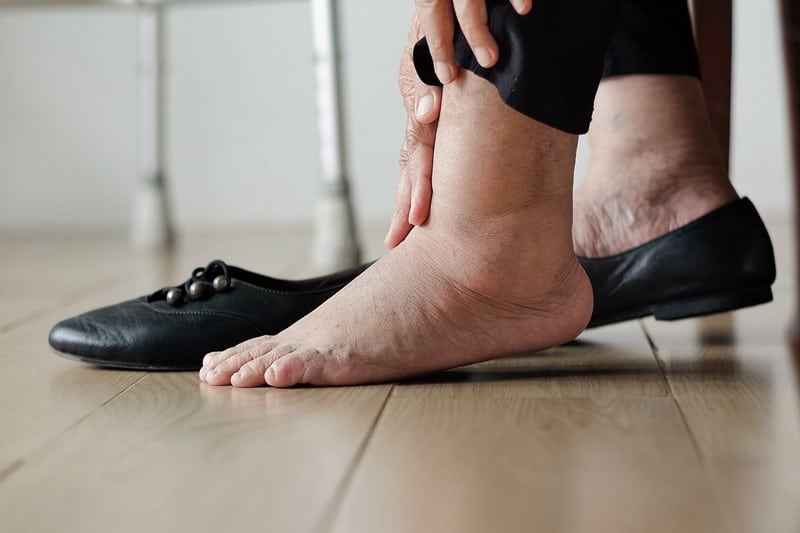
Swelling is the abnormal enlargement of human tissues such as organs, skin, or other tissues. Inflammation or fluid retention are common causes. External and internal swelling has the same effect on the body. Different medical issues may cause swelling. Bruising and swelling are common symptoms of many diseases, injuries, and insect bites. Inflammation inside the body might result from an adverse drug reaction or the aftermath of a severe injury. External swelling may be caused by inflammation in the body’s bones, tissues, or muscles.
Blood flow and microvascular function are two areas where histamine often does not significantly influence. However, mast cells inside the tissue may produce enormous quantities of histamine, which can have profound circulatory consequences following tissue damage, inflammation, and allergic reactions. Arteriolar vasodilation, venous constriction in certain vascular beds, and enhanced capillary permeability are all effects of histamine acting via H1and H2 receptors. These results involve increased blood flow to the area and swelling of the affected tissues. Swelling may be reduced by taking antihistamine medication that breaks down histamine in the body to achieve hormonal balance.










