Jaundice
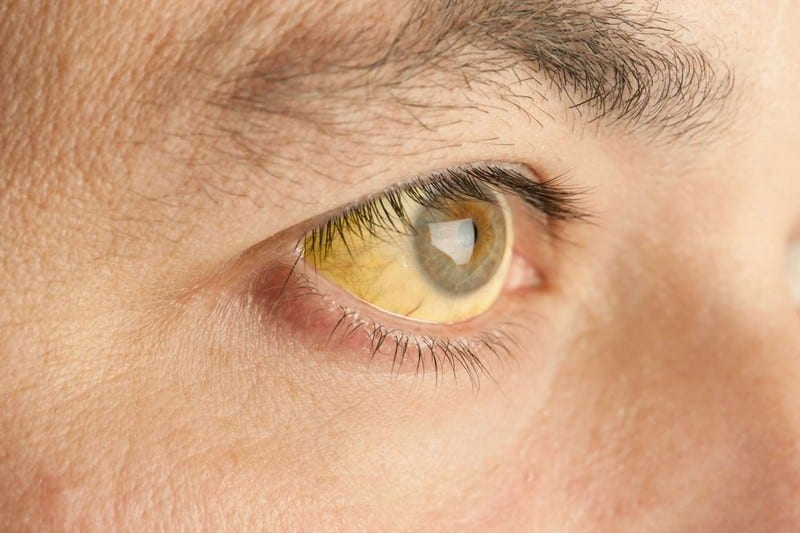
Jaundice refers to the medical condition where the eyes and the skin look yellowish. It usually happens when there’s an abnormal build-up of bilirubin in the blood. The three categories of the condition are pre-hepatic, hepatic, and post-hepatic jaundice. Some of the conditions that may lead to pre-hepatic jaundice are malaria, spherocytosis, and thalassemia. For hepatic jaundice, common triggers include liver cirrhosis, viral hepatitis, alcoholic hepatitis, leptospirosis, and liver cancer.
Lastly, post-hepatic jaundice may be caused by gallstones, pancreatic cancer, pancreatitis, and biliary atresia. Some of their accompanying symptoms may include abdominal pain, fever, weight loss, pale stool, dark urine, appetite loss, weakness, and diarrhea. Obesity, poor diet, genetics, tobacco and alcohol abuse, industrial chemical exposure, and specific conditions like diabetes can make one more vulnerable to jaundice.
Often, the treatment for jaundice will be based on its underlying cause. For example, if gallstones are causing the problem, lifestyle changes, treatments, and medications to dissolve the gallstones or surgical removal may be necessary. If it’s pancreatic cancer, chemotherapy and radiation may be used to destroy the cancer cells. In severe cases, surgically removing the cancerous tissues or the entire organ may be necessary. The key is to get treatment immediately.










