Salivary Gland Infection
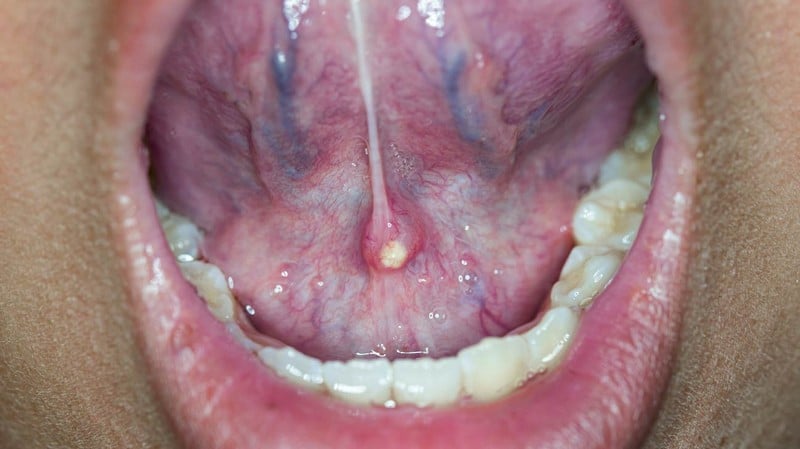
Salivary gland infection may also be the culprit for double chin. The salivary glands are hard-working laborers in the background. Each day, they produce up to one quart of saliva. This aids in digestion and guards against tooth decay. However, the glands occasionally have difficulty letting all that saliva flow out effectively. As a result, the area swells up, leading to a double chin.
Bacteria, particularly Staphylococcus aureus (staph), are the most frequent causes of acute salivary gland infections. The glands may become infected by viruses and fungi as well. The parotid glands can become infected with viruses, such as mumps.
Symptoms can include pain, tenderness, redness, fever, and chills. It also involves the discharge of infectious fluid from the gland and hard enlargement of the salivary gland. The condition is more likely to develop when the mouth is dry because of a salivary stone, insufficient fluid intake, and Sjögren’s syndrome (an immune system disorder that causes drying of mouth and eyes).










